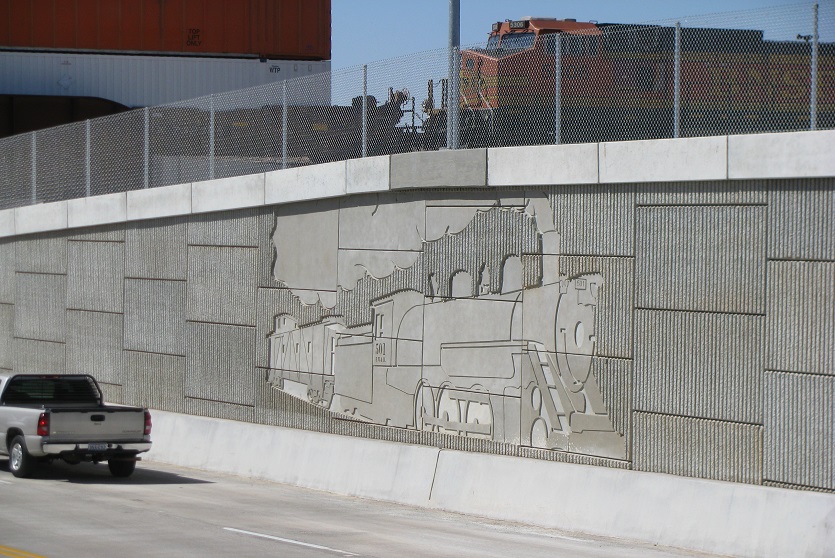
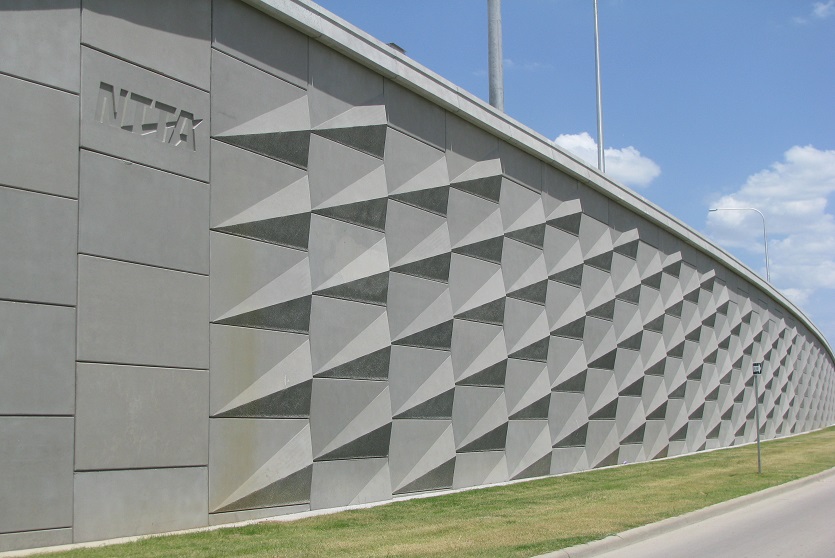
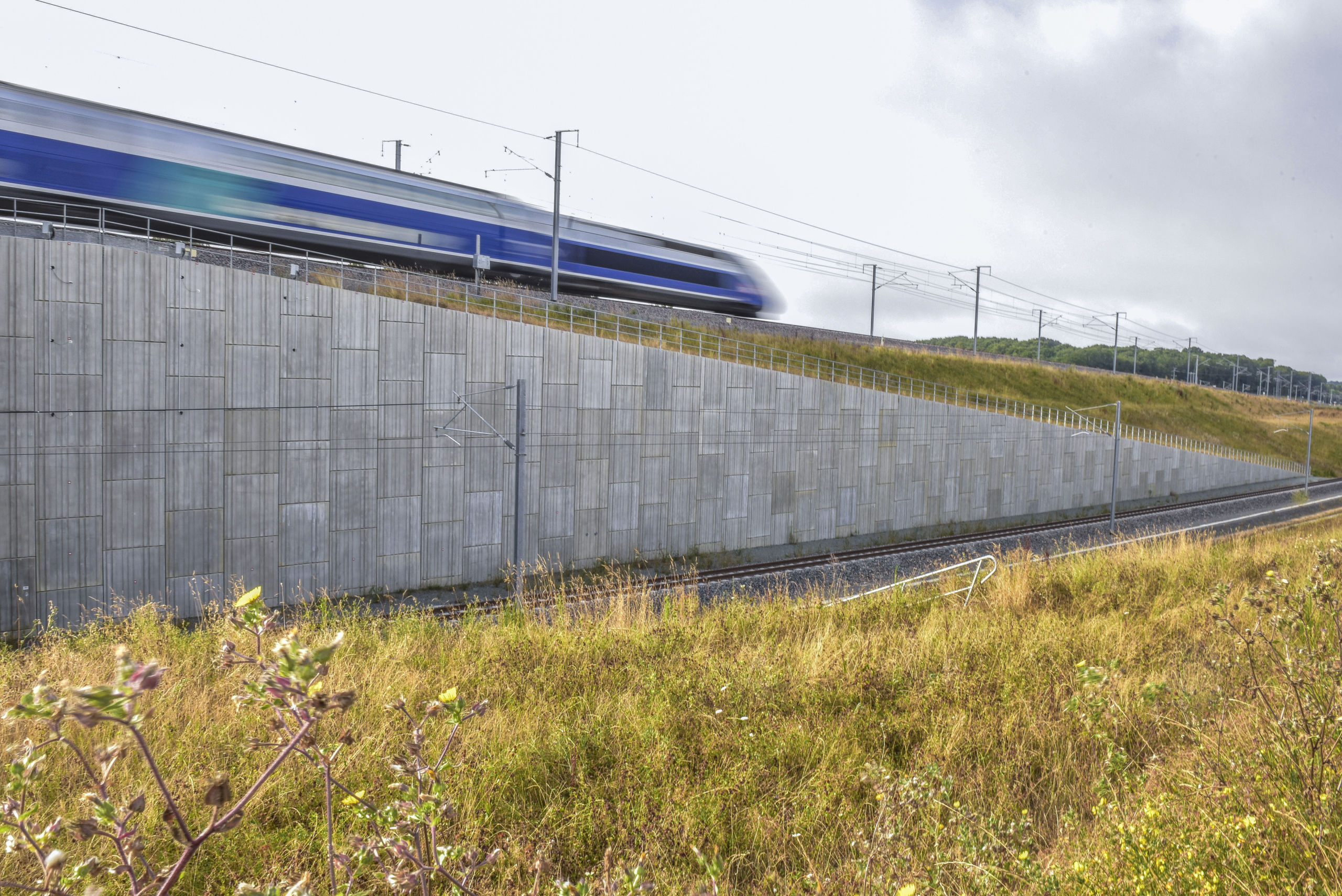
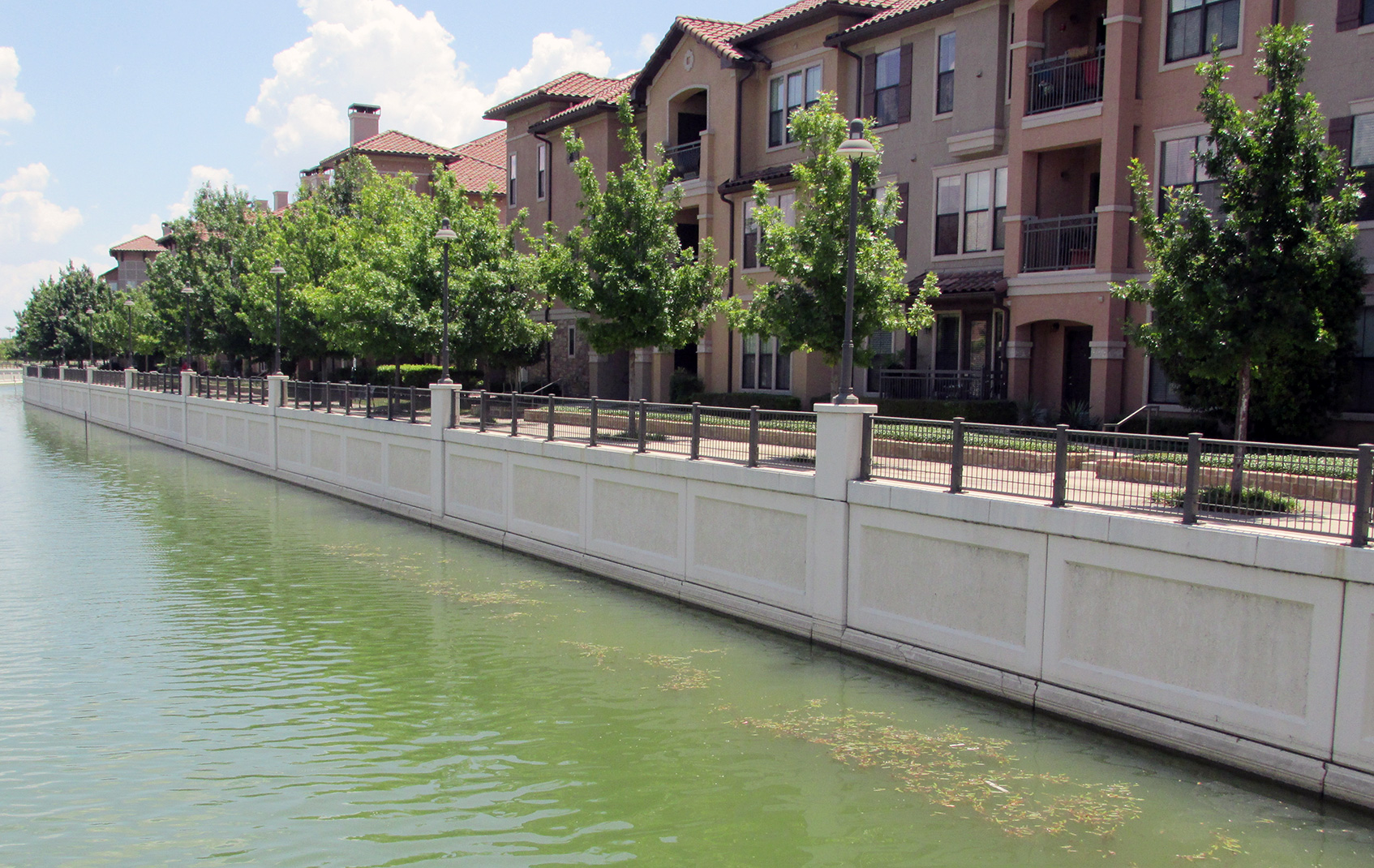
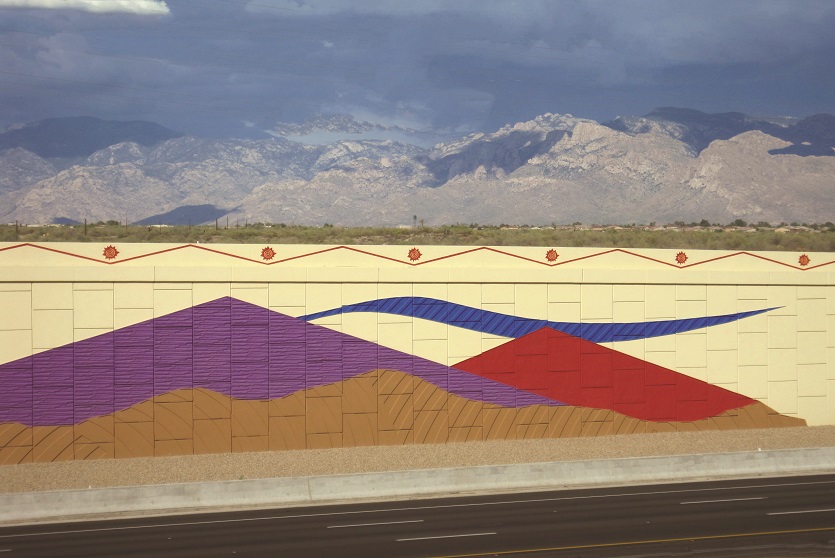
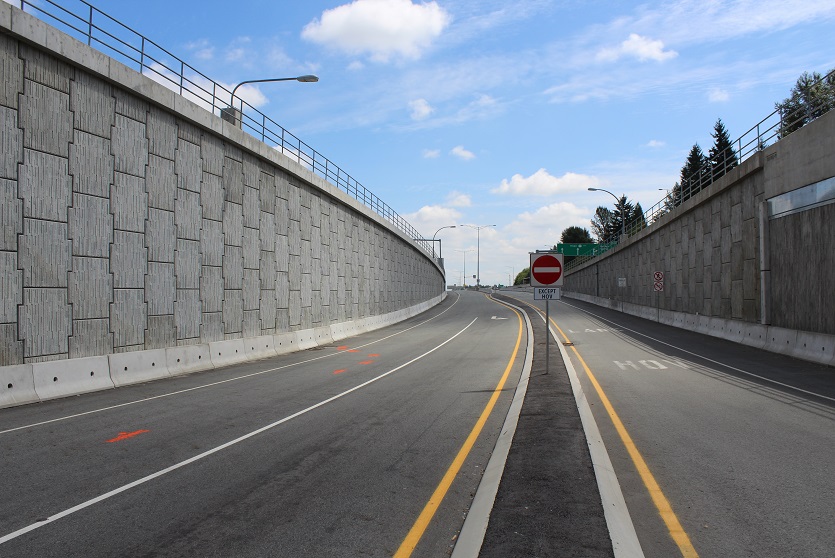
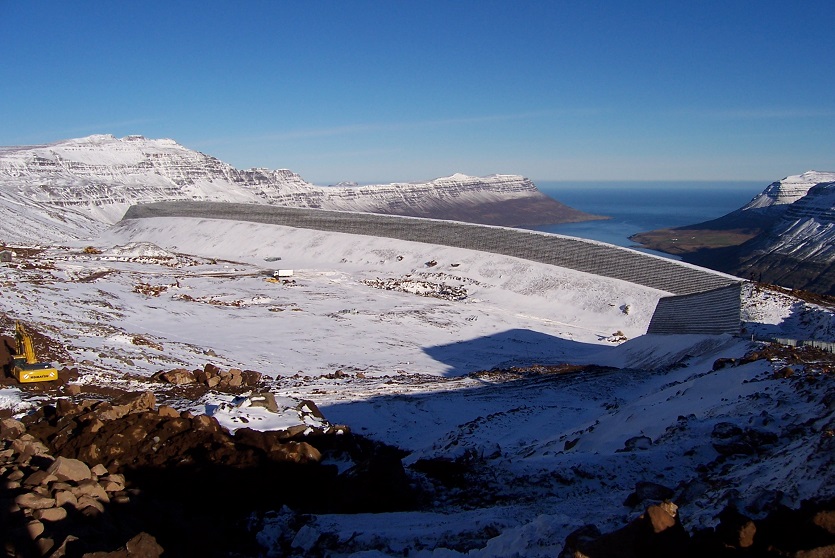
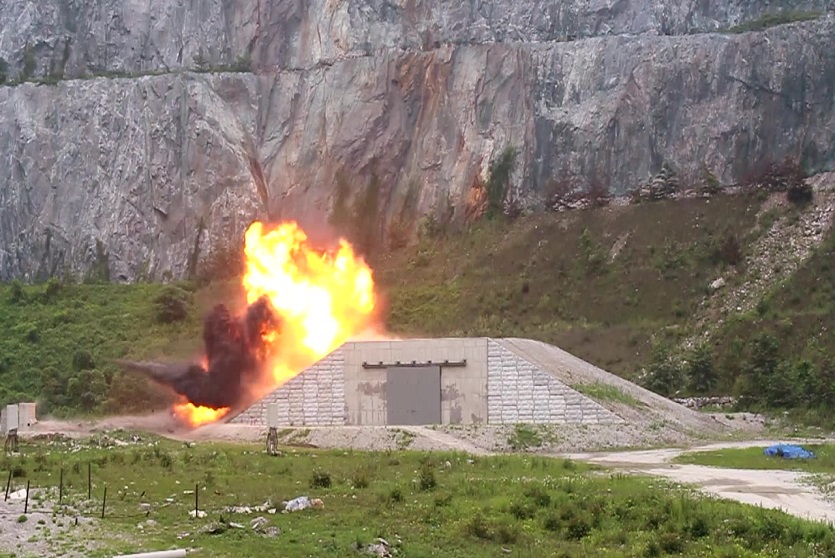
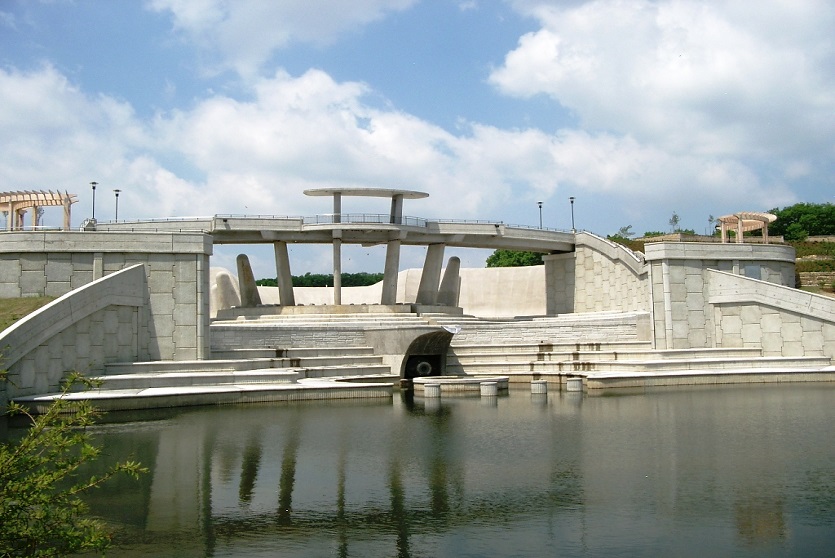
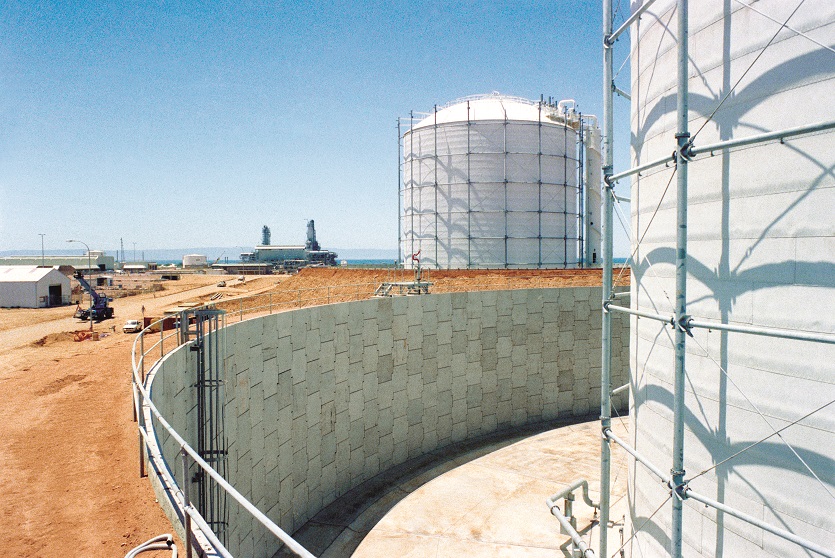
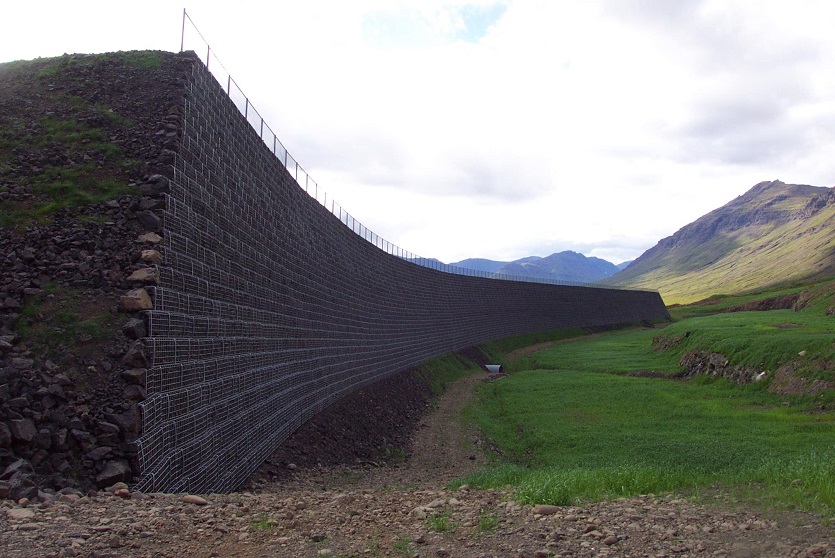
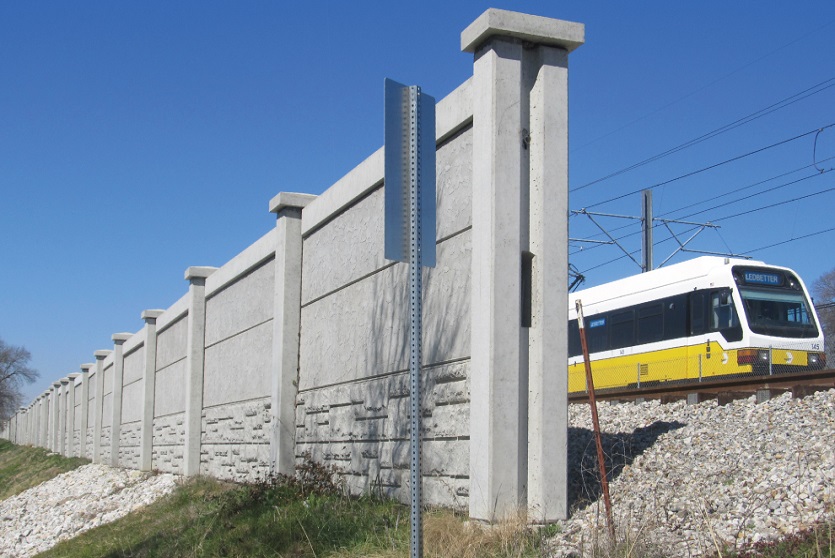
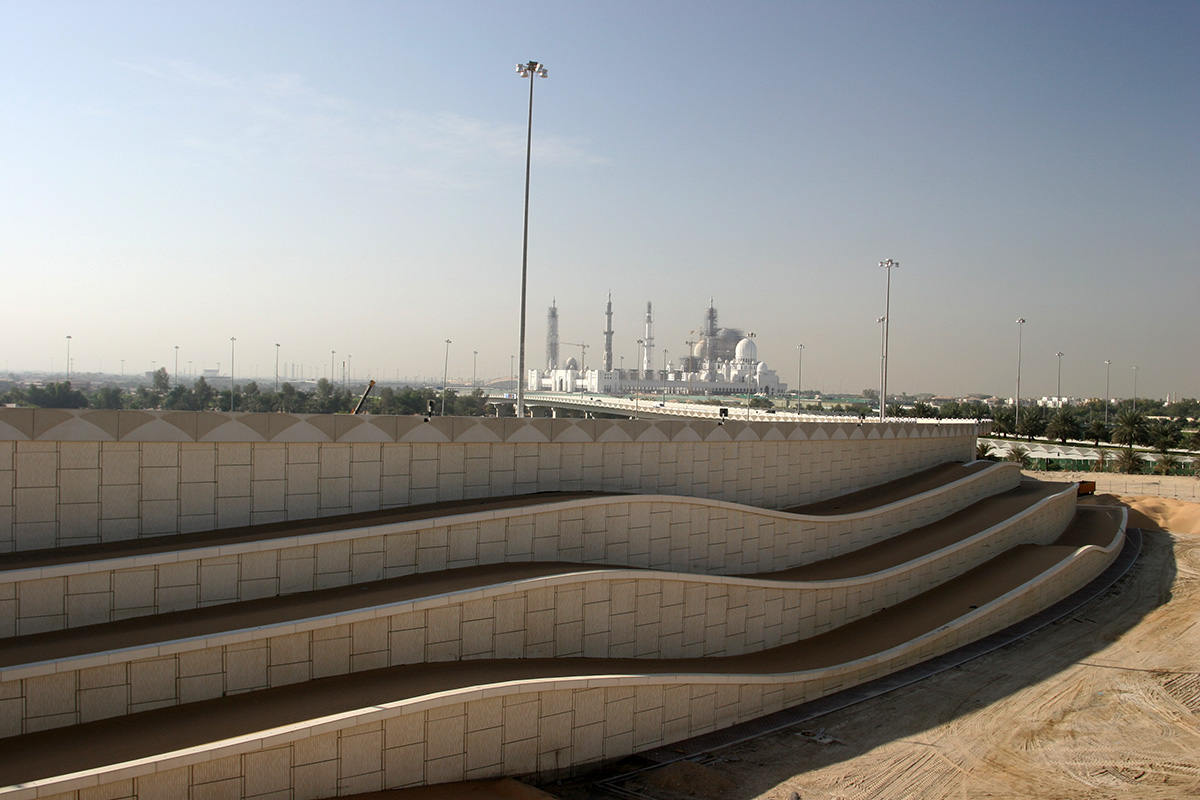
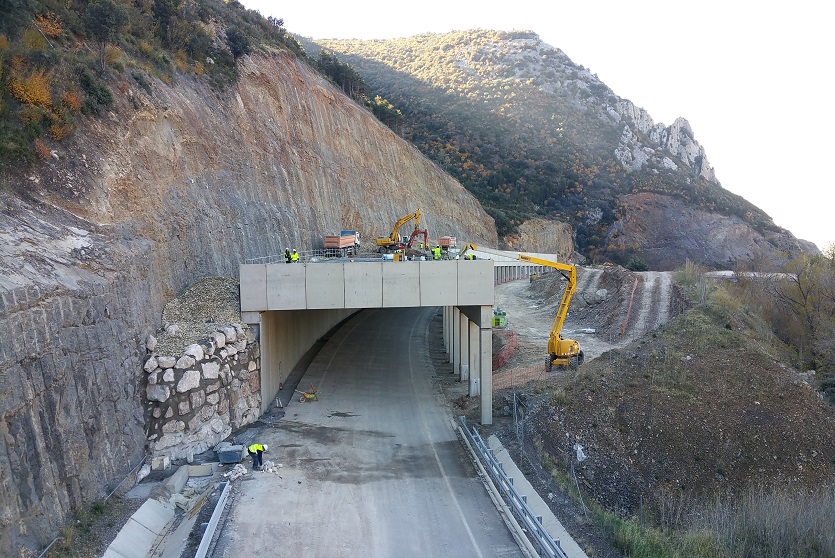
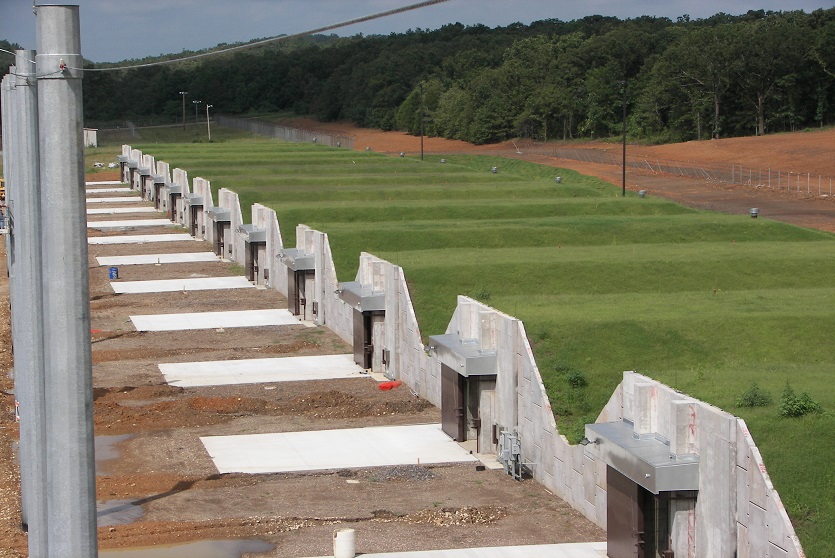
Reinforced Earth, first choice for retaining walls.
Reinforced Earth solutions have long been the first choice for engineers designing earth retention, retaining walls and ground stabilization, and for solving any soil-structure interaction design challenge.
Complex structural requirements
Installation and site adaptability
Environmental and aesthetic constraints
The original Reinforced Earth, a signature innovation
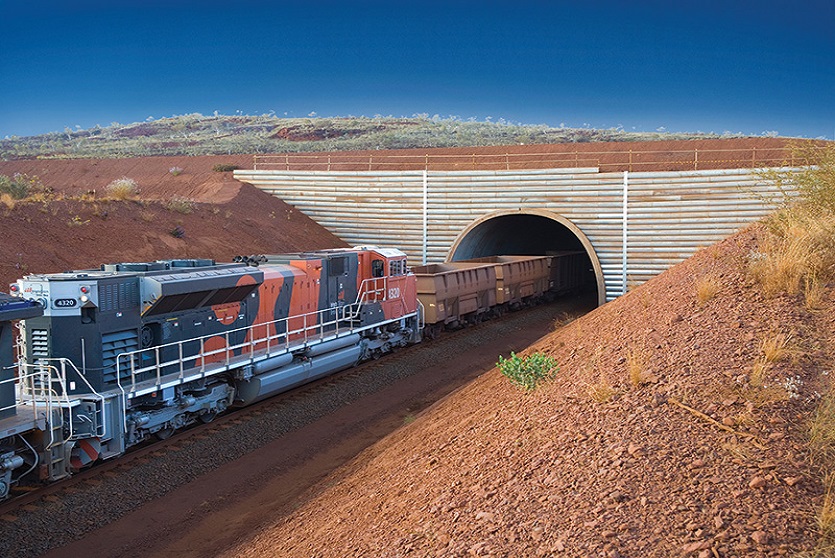
First pioneered by Terre Armée, the concept of mechanically stabilized earth walls (MSE) extends itself to an array of applications. Our engineers work with your team to apply this globally-recognized solution to solve nearly any geotechnical challenge you face in building roads, bridges, embankments, industrial landscapes, and more. Together, we will solve problems that arise when you are seeking solutions for your soils and structure interaction.
Concept description
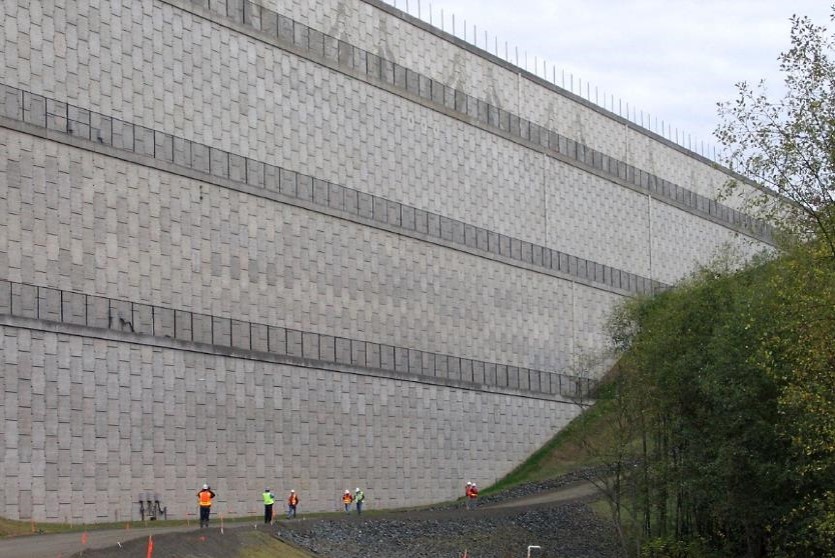
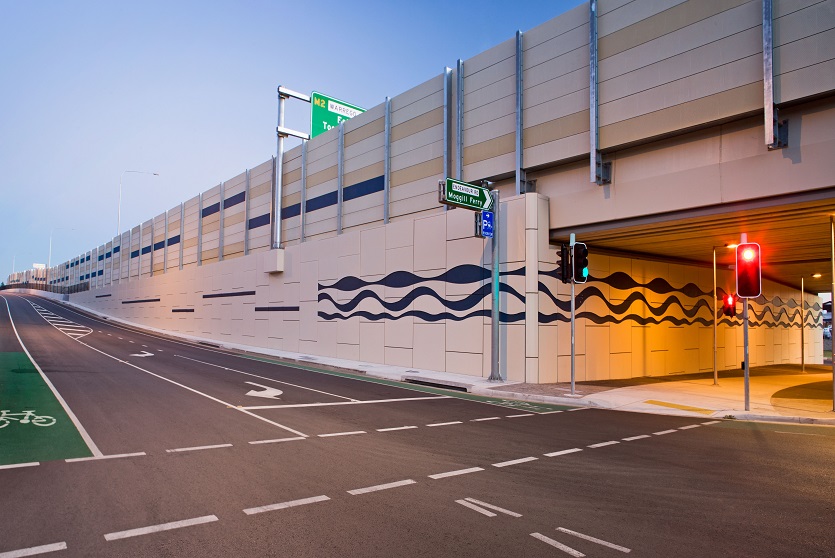
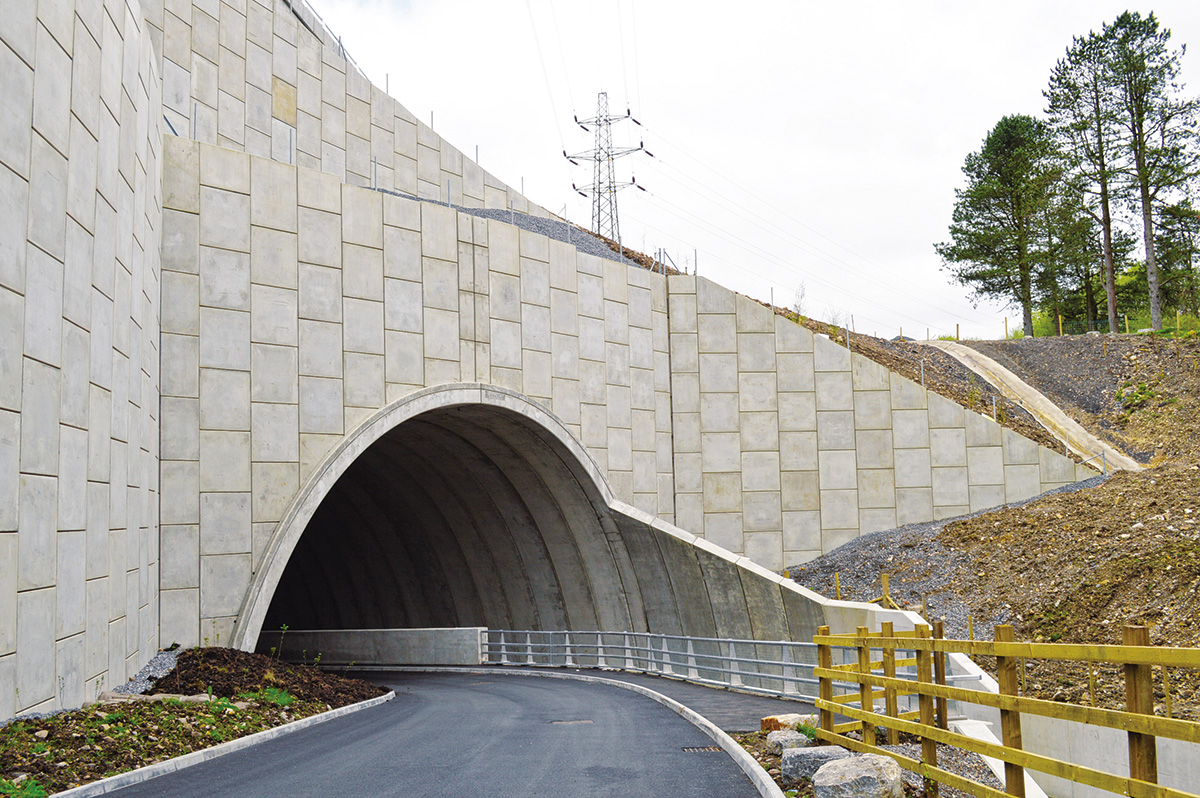
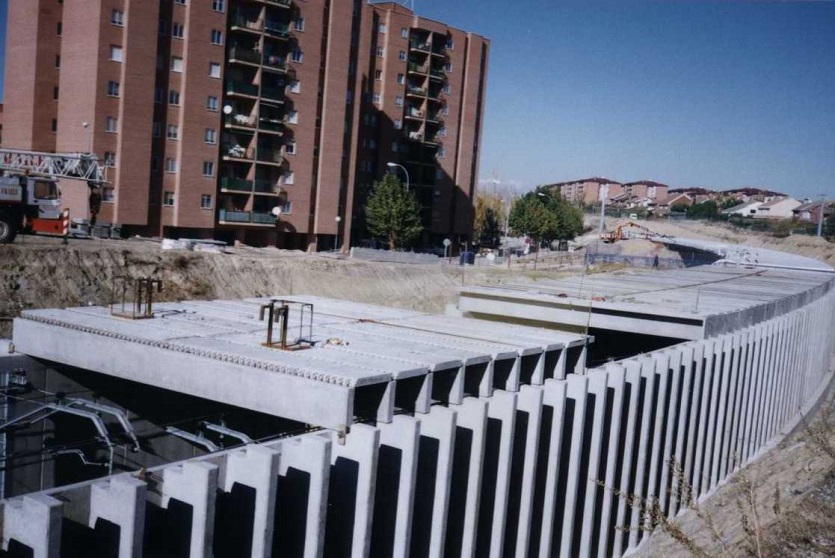
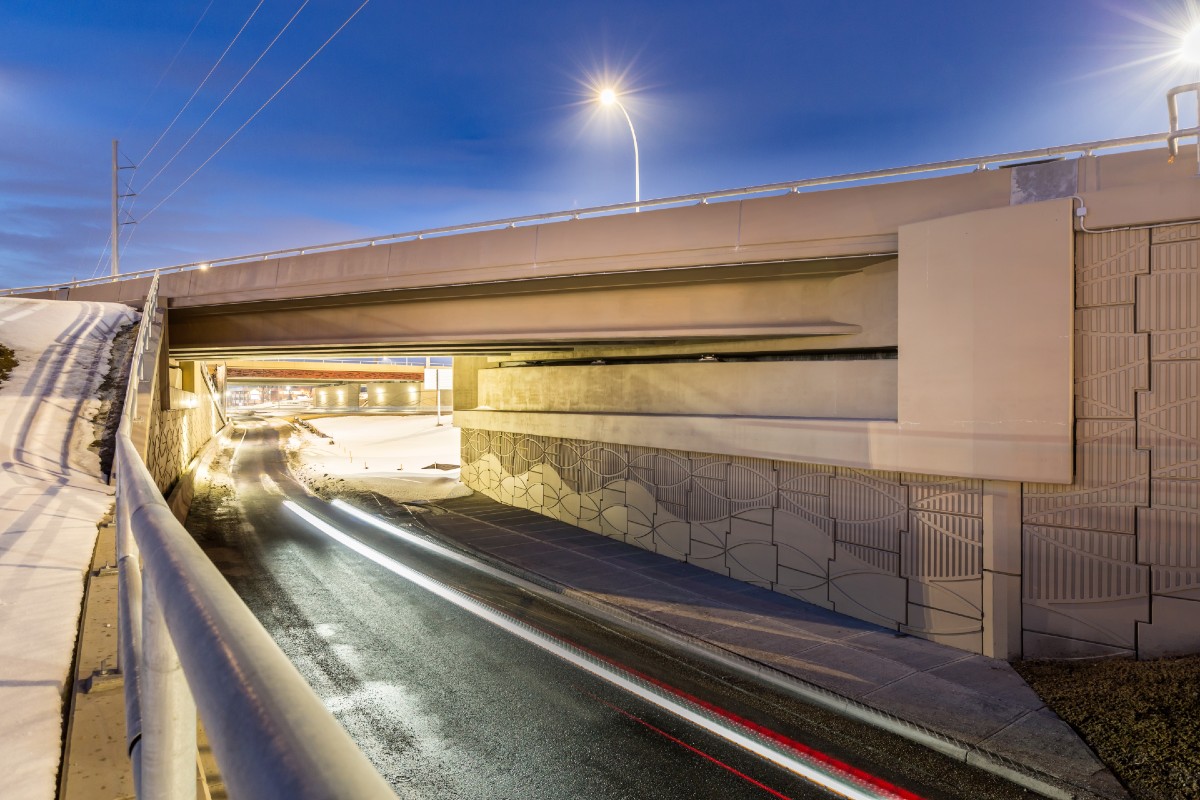
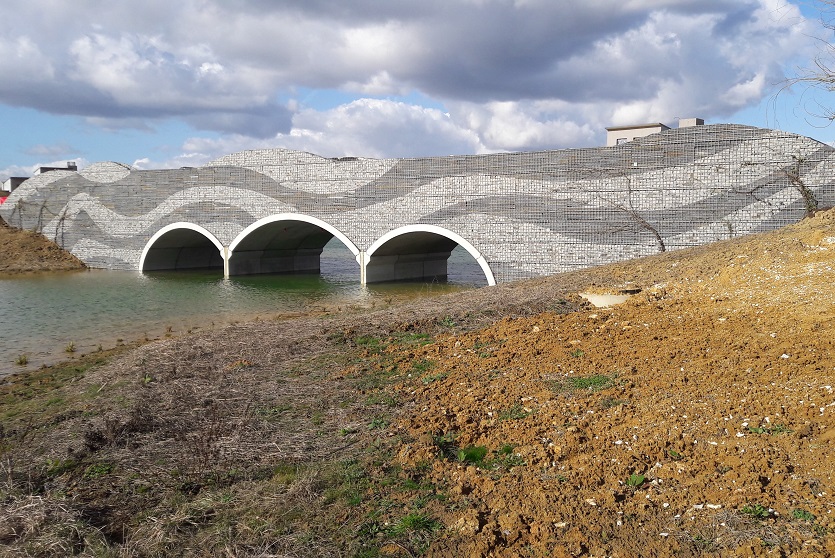
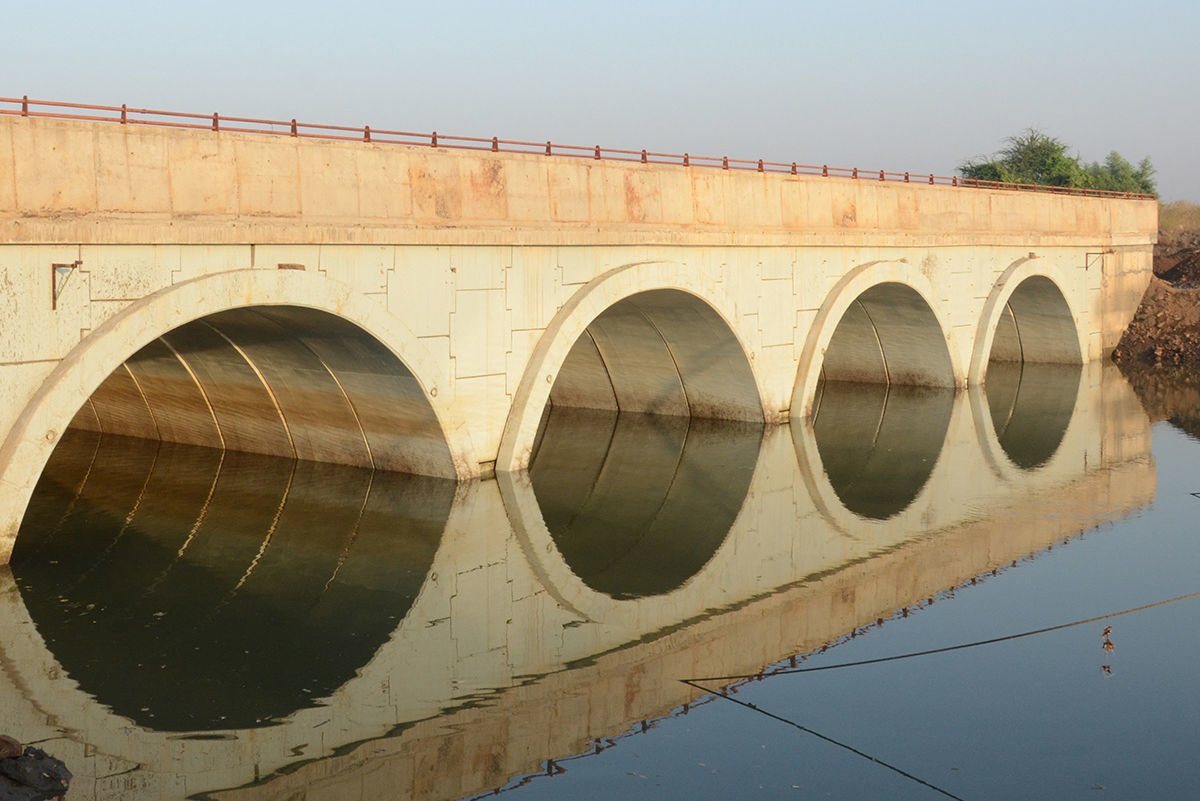
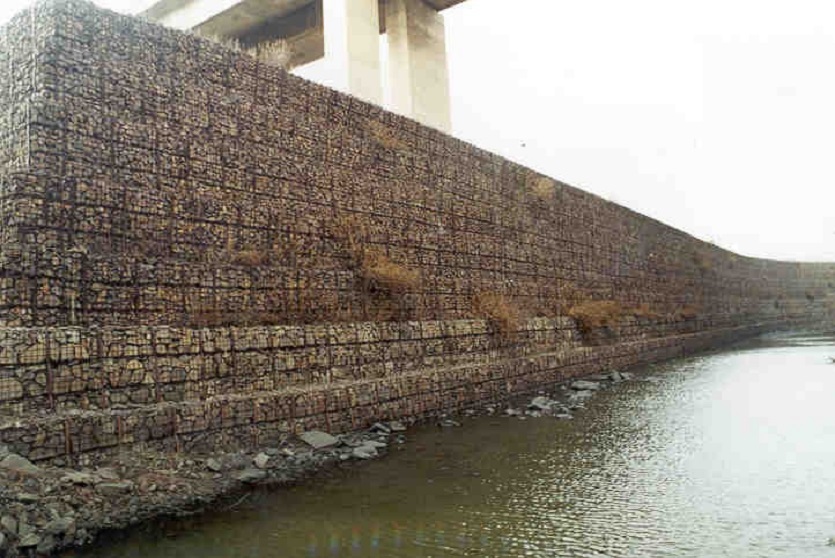
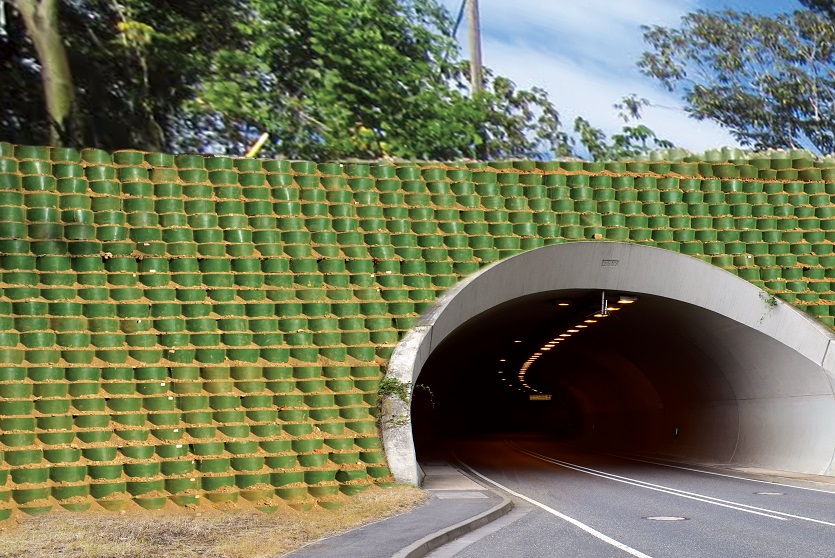
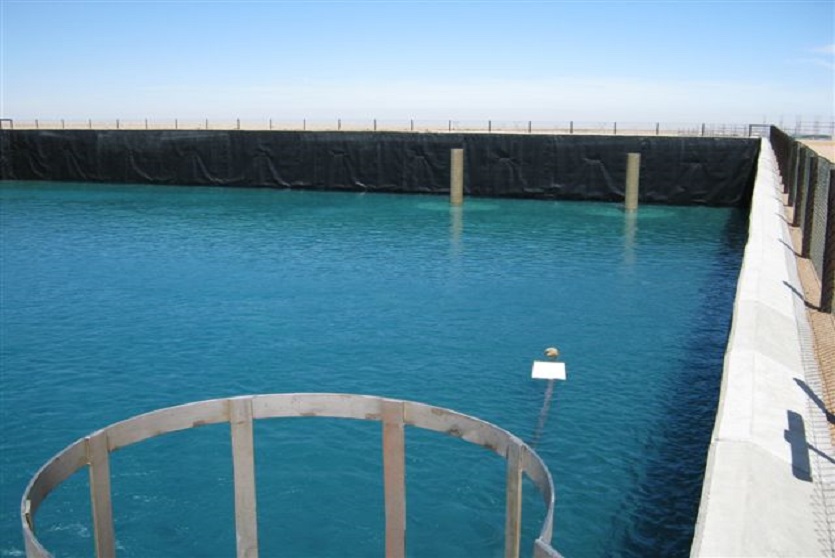
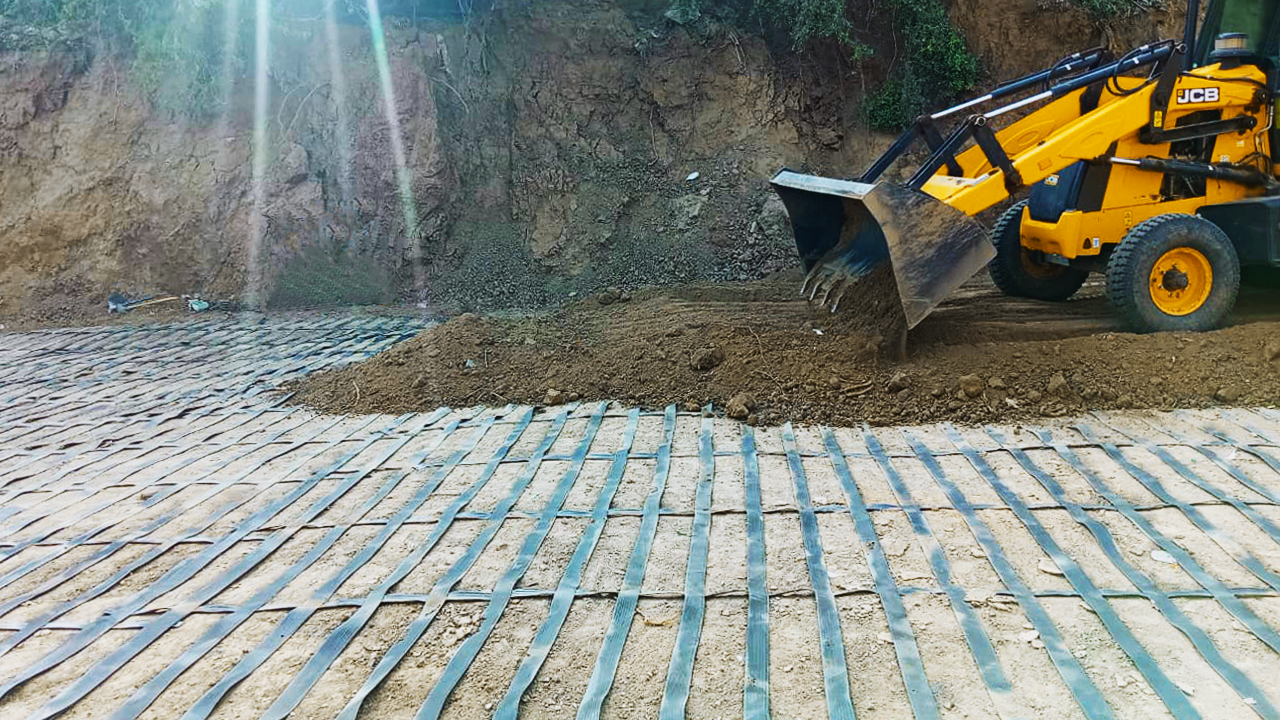
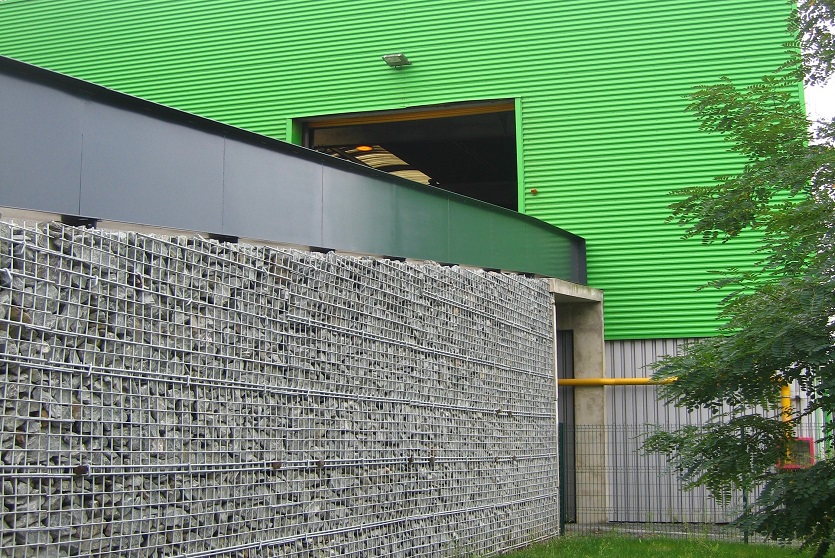
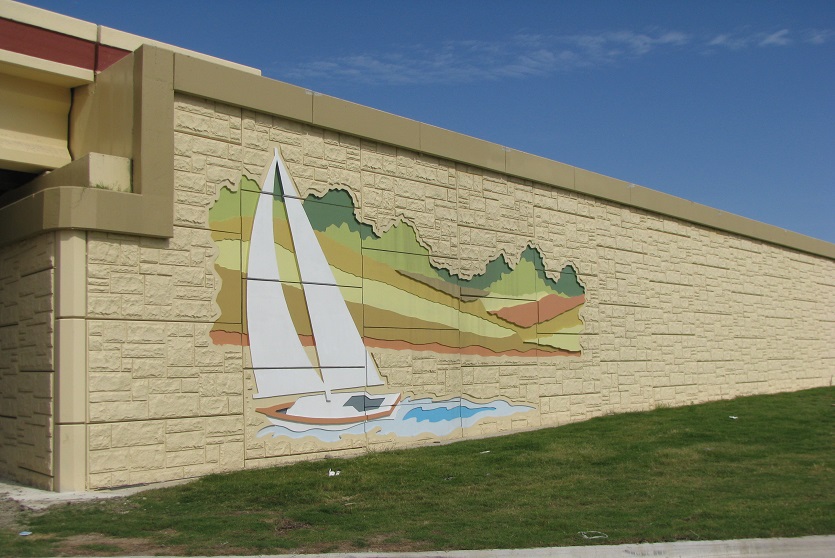
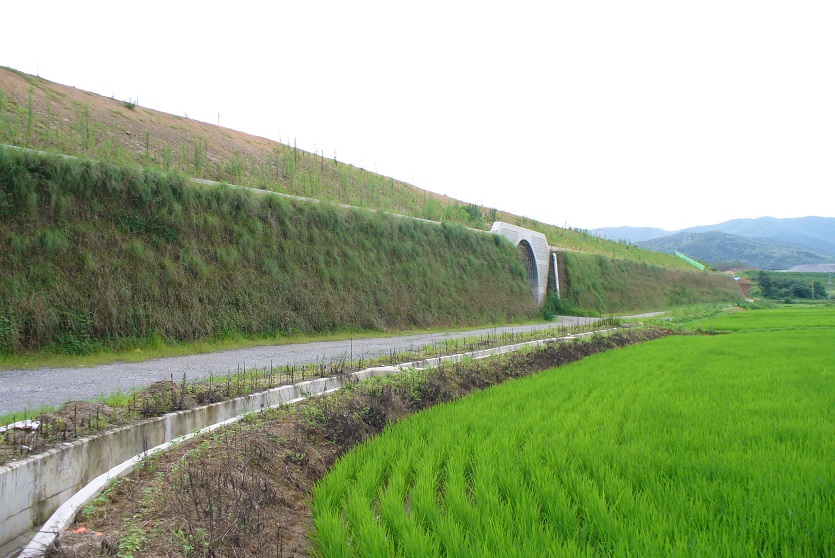
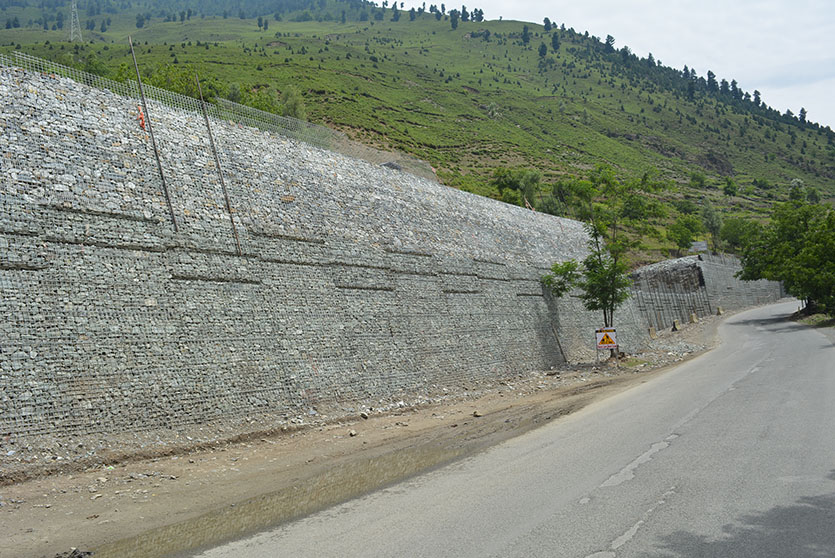
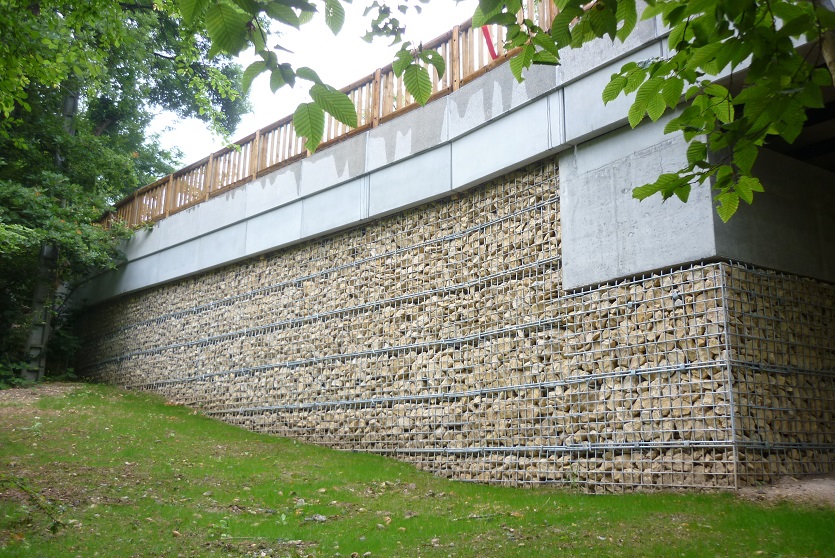
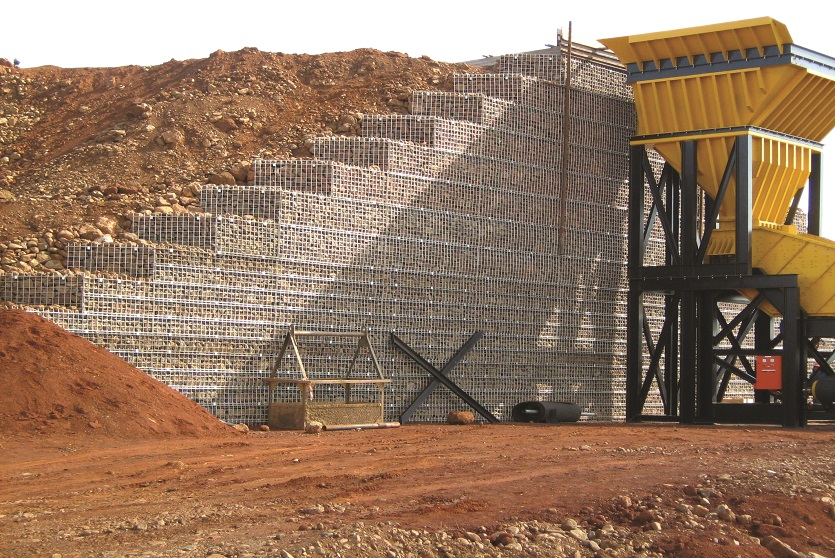
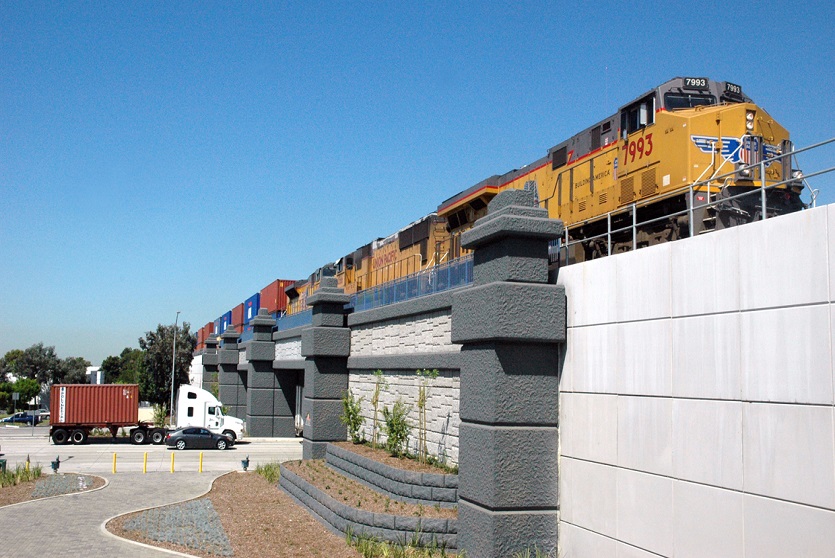
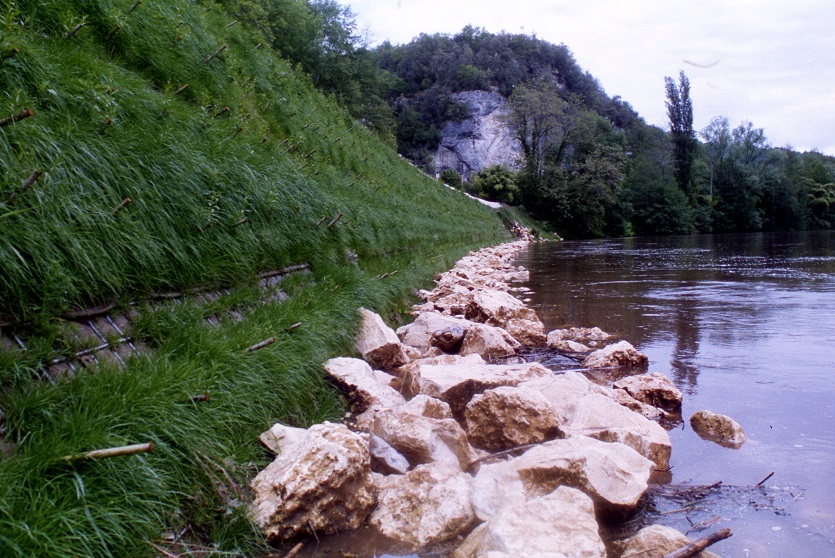
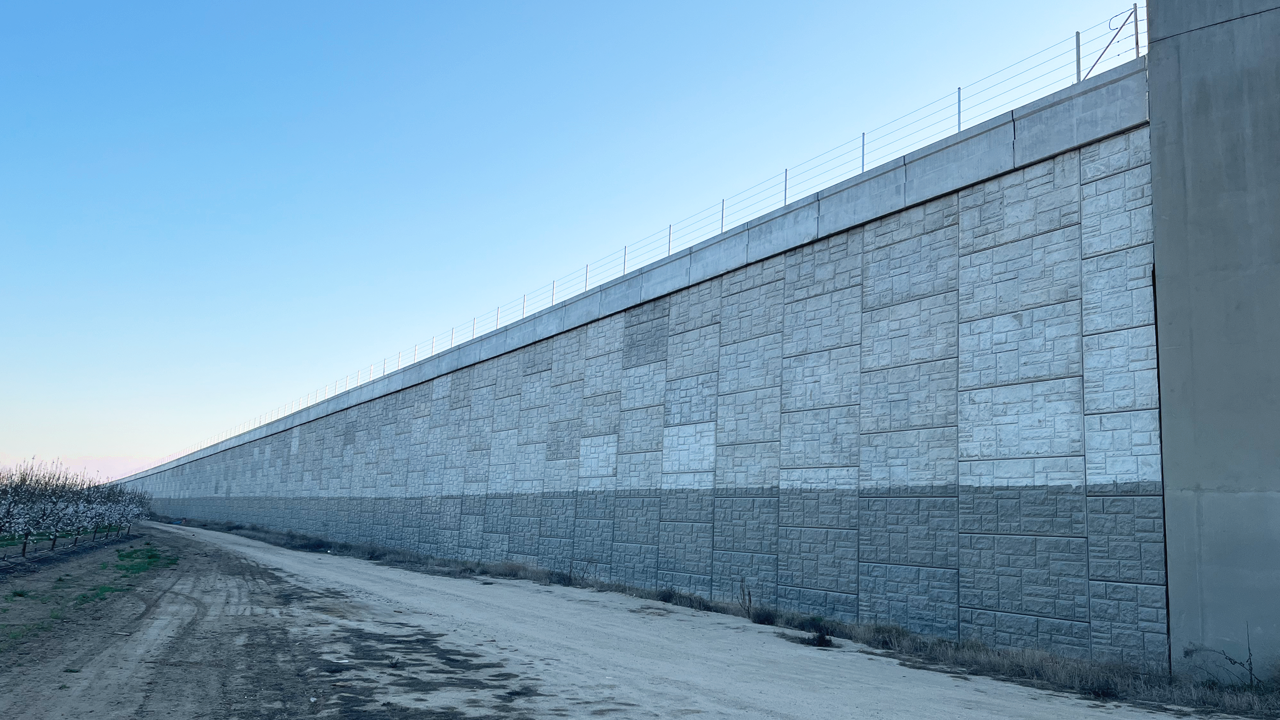
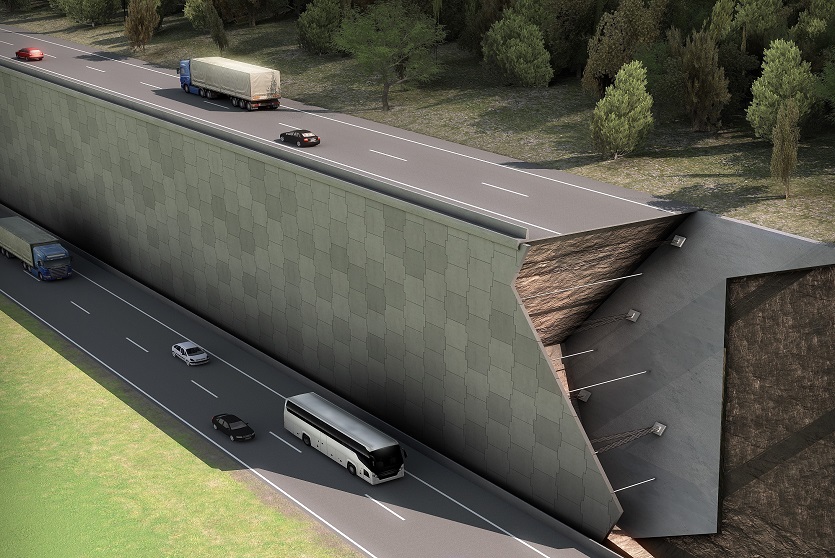
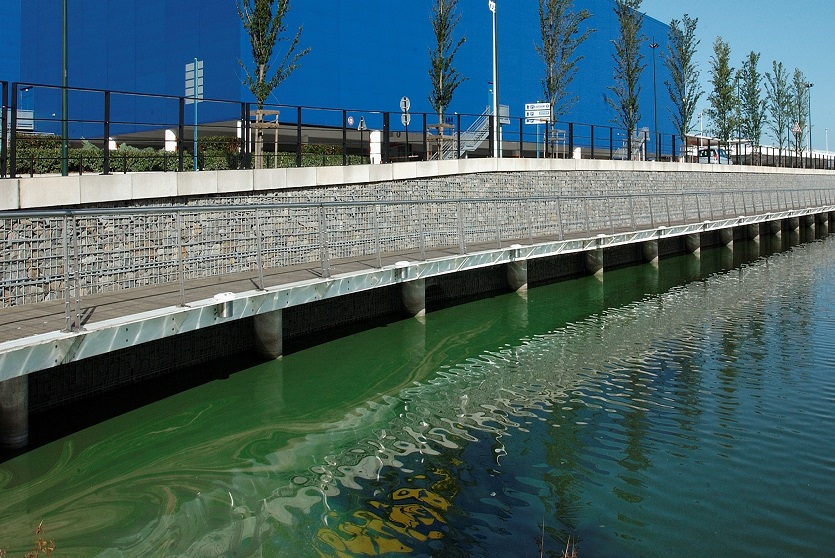
A resilient retaining wall solution, MSE structures combine controlled backfill with a selection of steel or geosynthetic soil reinforcements that are attached to a modular facing system. Facing systems vary, and may consist of concrete panels, wire mesh, vegetative surfaces or semi-elliptical metallic panels. The ideal combination of earth, soil reinforcements and facing creates a sustainable reinforced soil structure.
Design options and materials
Our professional engineers design Reinforced Earth structures with checks for internal and external stability, considering the static loads and the predicted dynamic loads. We optimize the design for your project using a calculative choice of materials and proper quantities that suit your specific plans for use and intended service life.
Our decades of experience have allowed us to expand the range of design options allowing our solutions to adapt to project and site constraints. Our Reinforced Earth structures can in fact be designed with precast concrete facing panels with various dimensions available, and using steel or geosynthetic reinforcements.
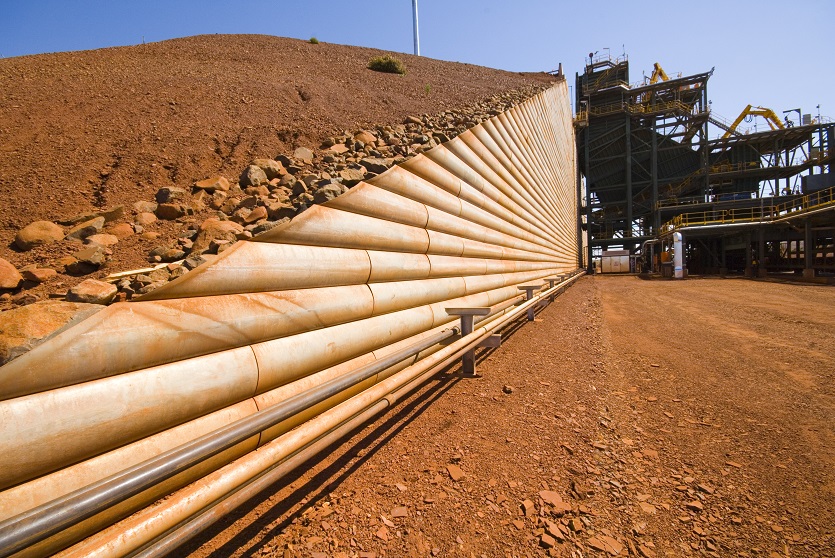
Our steel soil reinforcements have been designed and tested to optimize the pull-out and tensile capacity for various types of backfill. The reinforcing strips are patterned with “ribs” to optimize bonding with the compacted backfill. Our welded wire bar mats are used for efficiency in low-height walls or lightweight backfill situations where tension is low and extra pull-out capacity is needed.
Corrosion protection for all components in the form of galvanization is included when necessary to achieve a design life of 75 years, 100 years, or more. For temporary walls, using black steel is an option.
Our geosynthetic reinforcements are selected based on the characteristics of the intended backfill to be used, load factors, required service life and other considerations, engineers select from our four main categories of geosynthetic soil reinforcing strips:
- GeoStrap: Coated polyester (PET) strips without high-adherence edges, best for low pH backfill
- HA GeoStrap: Coated polyester (PET) strips with high-adherence edges, best for low pH backfill
- EcoStrap: Coated polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) strips without high-adherence edges, best for high pH backfill
- HA EcoStrap: Coated polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) strips with high-adherence edges, best for high pH backfill
Our solution allows:
Strength & durability
High structural integrity with strong load-bearing capacity for static and dynamic loads.
Vibration & seismic resistance
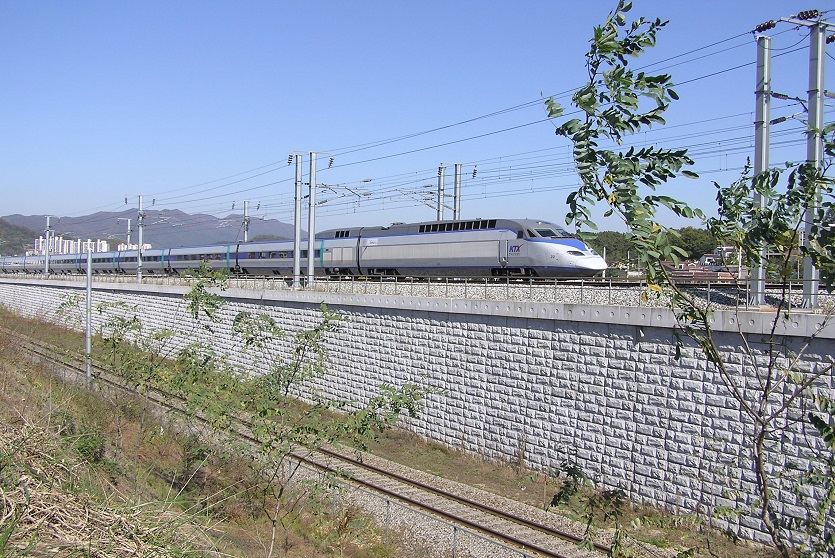
Absorbs industrial, railway vibrations and withstands earthquakes, even on poor foundations.
Cost & time efficiency
Reduces overall project costs through material efficiency, minimal upkeep, and fast installation.
Sustainable & space-saving
Low environmental footprint, efficient land use, and supports green/landscape designs.
Design flexibility
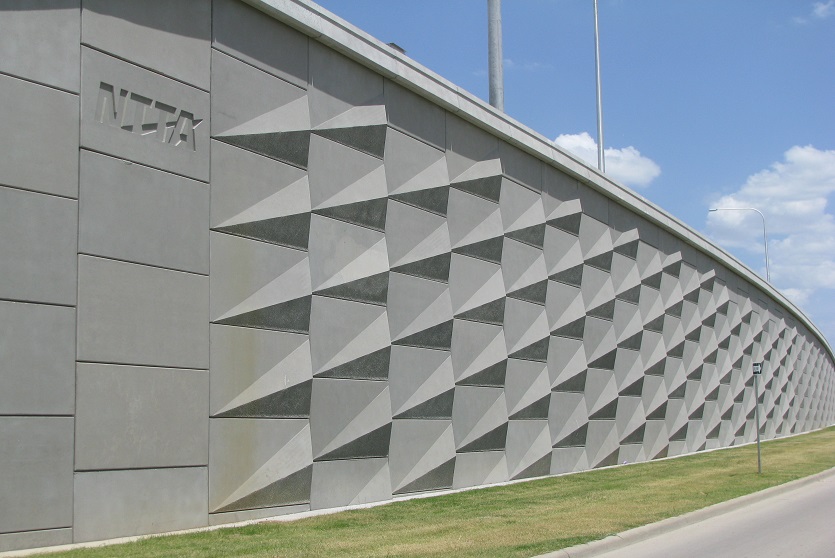
Customizable shapes, finishes, and textures to meet diverse architectural needs.
Our solutions suit severall applications to: RetainCrossProtectStrengthen